What is a Pick and Place Robot?
A pick and place robot is a type of industrial robot designed to automate the process of picking up items and placing them in a designated location. These robots are commonly used in manufacturing, packaging, and assembly lines to enhance efficiency, accuracy, and speed. By automating repetitive tasks, pick and place robots free up human workers to focus on more complex and value-added activities.
How Do Pick and Place Robots Work?
Pick and place robots operate by following programmed instructions to move items from one location to another. These robots are typically mounted on a stable base and can be programmed to perform specific tasks repeatedly with high precision.
Types of Movements and Tasks:
- Linear Movements: Moving objects in straight lines, often used in packaging and assembly lines.
- Rotational Movements: Twisting or reorienting objects, essential in applications where the object’s orientation is critical.
- Complex Movements: Combining multiple axes of motion to handle tasks requiring more flexibility and precision.
Types of Pick and Place Robots & Their Applications
Robotic Arm Types
Robotic arms are what first come to mind when thinking about pick and place robots, and they really are the most common. The technology has advanced to provide a range of options. Most robotic arms have five or six axes (joints), but they can have more or less.
Traditional robot arm axes move along one axis—either up and down, or left to right—but advanced robot arms have joints that can rotate and spin. These are called articulated robot arms, and most closely match the capabilities of a human arm.
5-Axis vs. 6-Axis Arms
Pick and place robots with 5-axis and 6-axis arms differ primarily in their range of motion and versatility. A 5-axis robotic arm can move in five different directions, making it suitable for tasks that require less complex movements, such as simple assembly or packaging tasks where the object doesn’t need to be reoriented.
In contrast, a 6-axis robotic arm offers an additional degree of freedom, allowing for more complex movements, including tilting and rotating objects. This added flexibility makes 6-axis robots ideal for applications that require precise placement and orientation adjustments, such as in electronics assembly or detailed product inspection.
Applications Suited for Each Type
- 5-Axis Robots: Used in straightforward pick and place tasks, such as picking items from a conveyor and placing them into boxes, where minimal reorientation of the object is needed.
- 6-Axis Robots: Suited for complex tasks that require more maneuverability, such as placing components on a circuit board or handling items with varying orientations and shapes.
Delta Robots
Delta robots, such as the PKR Robot, are known for their distinctive design, featuring a triangular configuration of arms that allow for high-speed, precise movements. These robots excel in tasks that require rapid picking and placing, making them ideal for industries where speed and accuracy are critical, such as food processing, pharmaceuticals, and electronics.
Unique Features
- Speed: Delta robots can handle hundreds of picks per minute, significantly increasing throughput.
- Precision: They are equipped with advanced vision systems that enable them to accurately identify and sort items by size, shape, and color.
Common Uses
- High-speed sorting and packaging of small items.
- Assembly tasks requiring rapid and precise movements.
- Applications in cleanroom environments due to their minimal contamination risk.
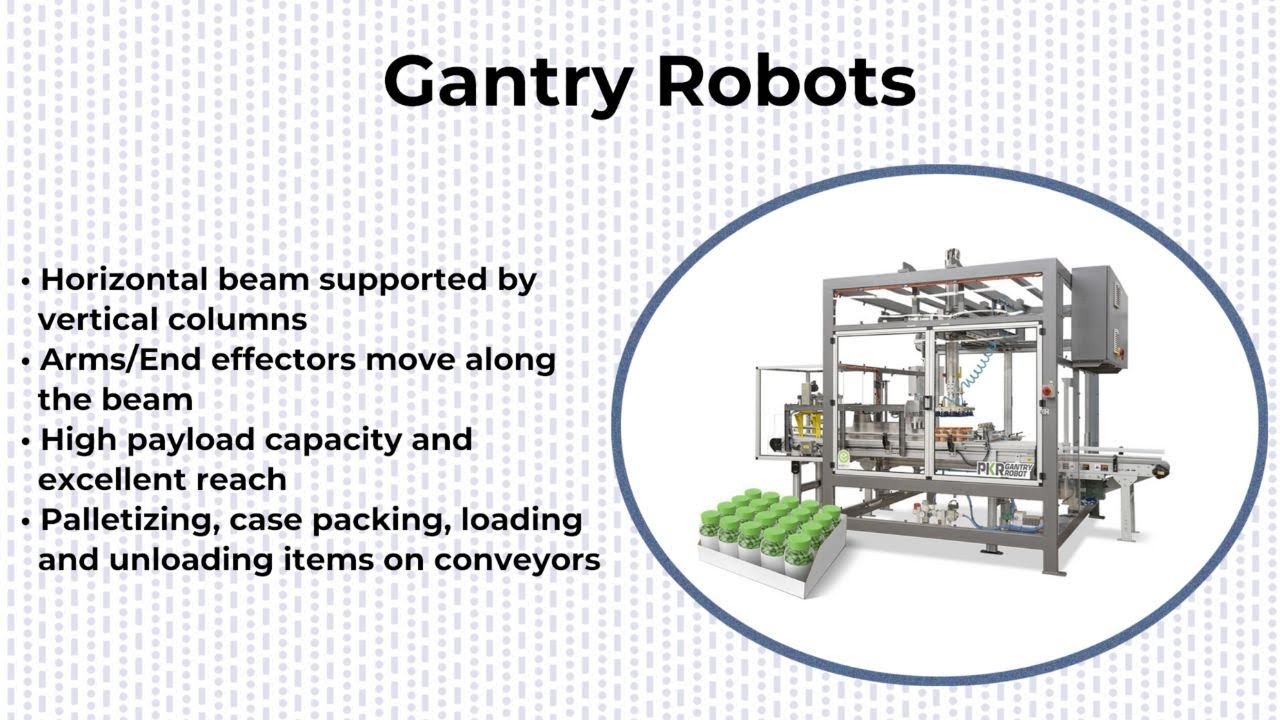
Cartesian/Gantry Robots
Cartesian robots, also known as gantry robots, operate along three linear axes (X, Y, Z) and are known for their simplicity and precision. They are particularly effective in tasks that require straightforward, linear movements and are commonly used in environments where space is a constraint.
Overview
- Structure: Consists of a rectangular framework that supports the robotic arm, allowing for movements along the Cartesian coordinate system.
- Applications: Often used in CNC machining, 3D printing, and pick and place operations in manufacturing settings where precise and repeatable movements are essential.
SCARA
Selective Compliance Assembly Robot Arms (SCARA) are similar to cartesian robots in that they work along three planes—X, Y, and Z axes. The difference is that two of their joints rotate, to allow for greater movement.
The term “selective compliance” indicates that they move well (they are “compliant”) along a horizontal plane, but not a vertical plane. SCARA robots have a great range of motion side-to-side, but not up and down.
This allows SCARA robots to be more accurate than cartesians. They are generally smaller robot arms, so best suited to smaller payloads. SCARA robots are favorite pick and place robots in pharmaceutical and electronics industries, where small items need to be placed with great precision.
Specialized Robots
Fast Pick Robots
Designed for high-velocity SKU operations, fast pick robots are tailored to handle items that need to be picked and placed quickly and efficiently. They are particularly useful in distribution centers and warehouses, where they can significantly reduce the time needed for order fulfillment.
Collaborative Robots (Cobots)
Cobots are designed to work alongside human workers, enhancing productivity and safety. These robots are equipped with sensors and advanced control systems that allow them to safely interact with humans, making them ideal for tasks that require a combination of robotic precision and human dexterity.
Applications for Specialized Robots
- Fast Pick Robots: Used in logistics for quickly assembling orders, particularly for items with high turnover rates.
- Cobots: Ideal for tasks such as picking and placing heavy or awkward items, leading workers through picking routes, and performing repetitive tasks that reduce worker fatigue.
Pick and Place Robot Applications
Pick and place robots are used in a wide variety of applications. Here’s a look at a few of the most common use cases for pick and place robots and how they’re used.
- Assembly – Pick and place robots are frequently used in assembly settings, where they select incoming parts from a conveyor or bin and attach it to another piece of the item.
- Bin picking – Pick and place robots are often used to find and select parts from bins. Machines in this application have advanced vision technology allowing them to analyze color, shape, and size.
- Inspection – Pick and place robots used for inspection feature advanced visual systems in order to grab objects, identify imperfections, and remove bad parts or items from the rest.
- Packaging – Pick and place robots are very often used for packaging. These machines select pieces from a belt or designated space and place the items in a tray, case, or other specialized packaging.
- Sorting – Pick and place robots with advanced vision systems are used for sorting in other industries, in addition to industrial bin picking. In the food and beverage industry they are used for sorting fruits and vegetables.
Pick and Place Robot Benefits
Pick and place robots are used in industries like manufacturing, warehousing, pharmaceutical, food and beverage, electronics, and more. They offer many benefits in each setting, including:
- Speed – Fast pick robots are the quickest, but most pick and place robots work at greater speeds than humans can.
- Efficiency – In addition to working faster, pick and place robots don’t need breaks. They can work faster, longer.
- Consistency and accuracy – People make mistakes for lots of reasons, but robots don’t. The simpler the task, the more easily it can be automated and error rates reduced or eliminated completely.
- Compact – While designs vary, pick and place robots are often small in size and lightweight, making them ideal for use in applications where space is limited.
- Safety – Outsourcing repetitive work, especially in dangerous industrial settings, to robots improves workplace safety.
- Productivity – In addition to faster, more efficient work, pick and place robots relieve humans of repetitive tasks and give them more time to innovate, strategize, and work on big-picture or creative opportunities.
How to Choose the Right Pick and Place Robot
There are a lot of options for pick and place robots, and these machines can automate a wide variety of tasks.
There are several key factors to keep in mind as you’re thinking about which type of pick and place robot will be the most helpful and efficient for your job and in your setting.
Axes
The axes are what set different types of pick and place robots apart from each other. More axes give greater range of motion, and more flexible/advanced axes compound those capabilities even more.
But that doesn’t always mean that more axes are better. More axes also increase the range of error, so consider the work you need done. Does the robot need freedom of movement or does it need precision? If the former, more axes is the answer. If the latter, fewer might be better.
Installation
Most pick and place robots install quickly and can start operating almost immediately. Still, be sure you understand the installation requirements, including how much space is needed and if any safety barriers need to be installed.
Flexibility
In addition to mechanical reach and configuration, consider how conceptually flexible you need the pick and place robot to be. Once it’s programmed to a task, how difficult is it to adjust?
Some robots are designed to do a limited number of tasks with a high degree of accuracy. If that’s all you need, that’s fine. But if logistics frequently change—if the robot will have to select from different size bins or or pack into a variety of package types, for example—you’ll need a more flexible program.
Integration
Consider your current operation’s physical spaces and software systems, and be sure you understand how well the pick and place robot you choose will integrate with both. Make sure the physical space is compatible with the robot’s requirements and that the software will integrate seamlessly with the systems your team is already using.
Most modern pick and place robots integrate well with almost any software system, but it’s worth double-checking before you make an investment.
Payload
Payload is the maximum weight a pick and place robot can safely manipulate.
Be sure to ask about and consider the weight of the robot’s arm and tooling as well. A pick and place robot needs to be able to accurately handle the heaviest item you have while its arm is extended.
Reach
Reach is the maximum distance at which the robot can work. Make sure the pick and place robot you consider can accurately reach what it needs to, but don’t overextend capacity—it needs to fit in your workspace as well.
- The maximum horizontal reach is the distance from the center of the robot’s base to the farthest point of its arm.
- The maximum vertical reach is the distance from the lowest point that the robot can reach to the highest.
Repeatability
Repeatability is a pick and place robot’s ability to place items with precision every time.
Some applications—like building electronics and placing small pharmaceuticals—require high repeatability. The right pick and place robot should meet the tolerance radius for your application within 0.5mm.
Speed
Any pick and place robot will operate faster than humans, but whether you’re automating for the first time or upgrading, consider how fast you need the robot to work at peak demand periods.
Spec sheets will usually indicate a robot’s speed in degrees per second.
Training
More advanced pick and place robots come with greater capabilities—and greater learning curves. More advanced machines generally require greater user training.
Be sure to understand how much training is required for an operator to make full use of the robot, how long that training takes, and how it is generally accomplished. You don’t want to end up with a sophisticated robot that no one can use.
Vision
Consider how much your pick and place robot needs to “see.” Locating and selecting one of many identical items doesn’t require the same vision technology as sorting through a collection of similar items, or inspecting items for discrepancies. The vision guidance system should be sophisticated enough to identify several items from a pool of SKUs.
Pick and Place Robot Costs
The cost of a pick and place robot depends on a lot of factors including which type of robot you need, installation requirements, and more. A simple machine can start automating your facility for only a few thousand dollars, and a more advanced system might cost ten times that.
When evaluating the cost of a pick and place machine, there are other considerations in addition to the price tag:
- Savings – Calculate how much work your chosen robot can complete in a month and compare that workload to current resource requirements. Many pick and place robots pay for themselves fairly quickly.
- Increasing returns – With proper preventative maintenance, a good pick and place system will run smoothly for decades. After the robot pays for itself in savings, the rate of return on your investment skyrockets.
- Low maintenance – Many pick and place robots require surprisingly simple maintenance. Many companies can care for these robots with in-house resources, which lowers their total cost of ownership.
Start your pick and place robot journey today
Investing in pick and place robots enables companies to gain a competitive edge and maximize the productivity of their facilities, and the team at EndFlex can help you get started.
We have over 30 years of industry experience with primary, secondary, and end-of-line packaging machines. We’re also proud of our national service presence, ability to provide systems integration, and an installed base that includes more than 7,000 machines across the world.
Pick and Place Robot FAQs
Q: What are the big robot arms called?
The big robot arms you may have seen assembling cars or assisting Tony Stark are called pick and place robots. There are many types of pick and place robots, but the most famous are collaboration robots with articulated axes.
Q: What is pick and place assembly?
Pick and place assembly is an automated manufacturing process that uses a variety of pick and place robots to to put together components along an assembly line.
Q: How do pick and place actuators work?
Pick and place machines may use a variety of actuators, including pneumatic, hydraulic, and rotary actuators. These are used to move arms, rotate parts, and apply the appropriate amount of pressure.